Introduction to kWh to MWh
Understanding energy conversion is crucial in today’s world, where energy efficiency and cost savings are paramount. One of the fundamental conversions in energy management is from kilowatt-hours (kWh) to megawatt-hours (MWh). But what does this conversion mean, and why is it significant?
At its core, converting kWh to MWh involves scaling up energy measurements from smaller, more common household units to larger, industrial-scale units. This conversion is not just a mathematical exercise; it holds practical implications for how we manage and optimize energy use across different settings. For instance, while a typical household might consume energy measured in kWh, a manufacturing plant or a regional power grid operates on a scale requiring MWh. This distinction is vital for accurate billing and effective energy planning.
Let’s explore why this conversion matters. Imagine a scenario where you’re trying to understand your energy bill or planning to optimize energy use in a factory. Knowing how to convert kWh to MWh allows you to scale your energy data appropriately, ensuring you have a clear picture of consumption patterns. This clarity is essential for making informed decisions about energy efficiency and cost management.
Moreover, in the realm of renewable energy, understanding these units can significantly impact project planning and implementation. For example, solar power outputs are typically measured in these units, influencing how energy savings and sustainability efforts are calculated. By mastering the conversion from kWh to MWh, you gain a valuable tool in your energy management toolkit, enabling you to navigate both everyday and large-scale energy scenarios with confidence.
In the following sections, we’ll delve deeper into the basics and applications of these energy units, offering practical tips and insights to help you make the most of your energy resources.
Understanding kWh to MWh Basics
When it comes to energy consumption, understanding the difference between kilowatt-hours (kWh) and megawatt-hours (MWh) is essential. These units of measurement are pivotal in both residential and industrial contexts. But what exactly do they mean, and how are they used?
Let’s start with the kWh definition . A kilowatt-hour is a measure of energy that represents the amount of work done by a power of one kilowatt operating for one hour. This is the standard unit used in household energy billing. For instance, if you run a 1,000-watt appliance for one hour, you have used 1 kWh of energy.
On a larger scale, we have the MWh definition . A megawatt-hour is 1,000 times larger than a kilowatt-hour, equating to 1,000 kWh. This unit is often used in industrial settings or when discussing the energy production of power plants and large-scale renewable energy projects. Understanding this conversion is crucial: 1 MWh = 1,000 kWh.
Common Uses of kWh and MWh
- kWh: Primarily used for household electricity billing and small-scale energy consumption tracking.
- MWh: Used in industrial energy consumption, power plant outputs, and large-scale renewable energy projects.
Imagine a typical household scenario: your monthly energy bill reflects usage in kWh, helping you track and manage your energy consumption efficiently. On the other hand, if you’re managing a factory’s energy use, you’ll likely deal with MWh, as it provides a clearer picture of large-scale energy consumption.
This understanding becomes even more critical when planning energy efficiency upgrades or integrating renewable energy solutions. For example, when assessing solar panel installations, knowing how to convert kWh to MWh can help you determine the system size required to meet your energy needs.
Grasping these basics not only aids in energy management but also empowers you to make informed decisions about energy efficiency and sustainability. As we move forward, we’ll explore the key differences between these units and how they impact energy planning and cost management.
Key Differences Between kWh and MWh
Understanding the distinction between kilowatt-hours (kWh) and megawatt-hours (MWh) is crucial for both residential users and industrial operators. These units, though related, serve different purposes depending on the scale of energy consumption. Let’s delve into how these differences manifest in practical scenarios and why it’s important to choose the correct unit for accurate billing and resource planning.
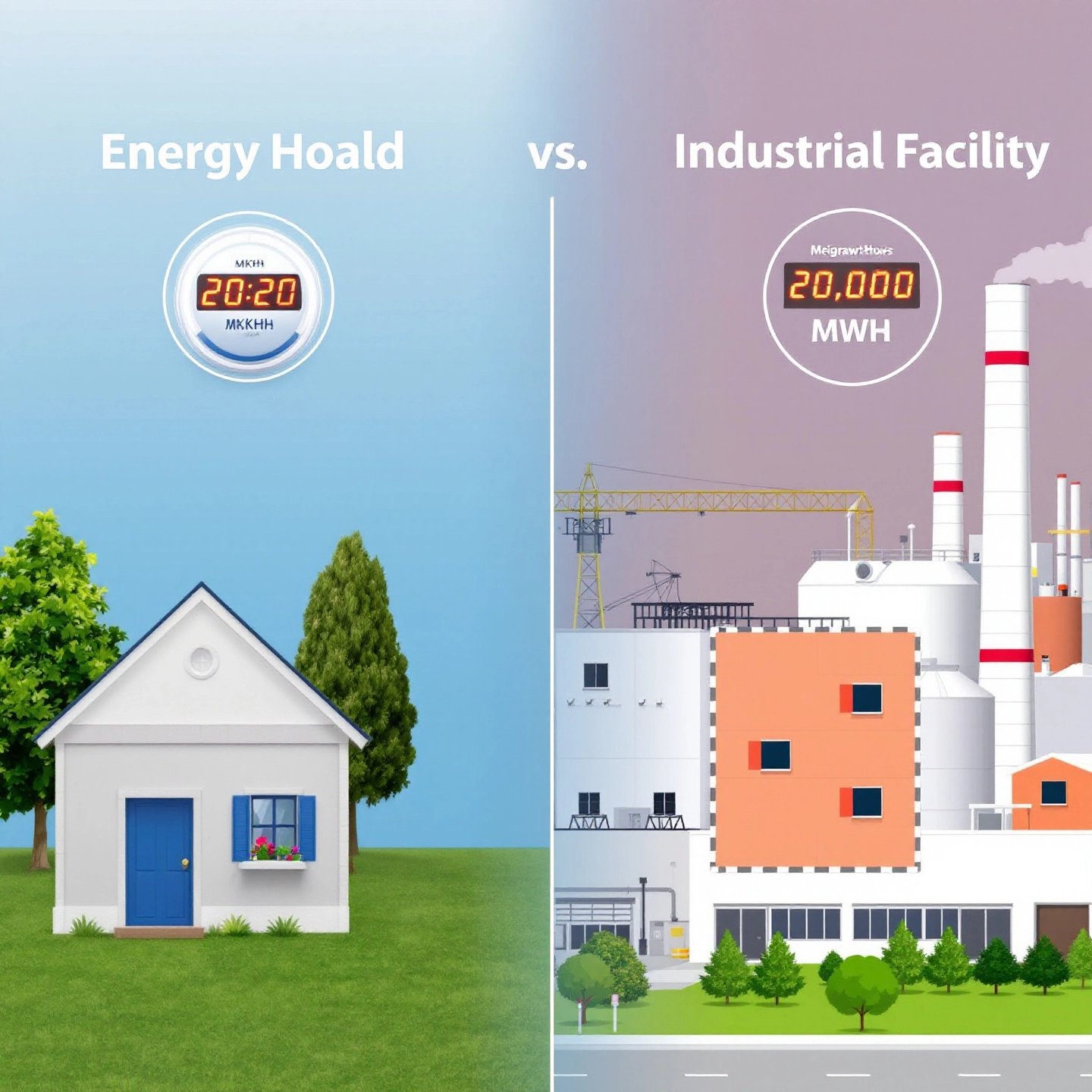
kWh vs MWh: A Comparative Overview
The fundamental difference between kWh and MWh lies in their scale. While kWh is a more familiar unit for individual households, MWh is essential for larger-scale operations. To illustrate this, consider the table below, which compares typical monthly energy usage:
| Usage Context | Typical Monthly Usage |
|---|---|
| Household | 914 kWh |
| Industrial Facility | 1,000 MWh |
As seen in the table, a household’s energy consumption is typically measured in kilowatt-hours, reflecting smaller-scale usage. In contrast, industrial facilities, which require significantly more power, measure their consumption in megawatt-hours.
Application and Importance of kWh vs MWh
Choosing the right unit of measurement is not merely a technicality; it has practical implications for energy management and financial planning. For households, using kWh helps in tracking energy consumption and understanding electricity bills. For instance, a typical U.S. household consumes about 914 kWh per month, which is manageable and easy to comprehend in kWh terms.
In industrial settings, however, energy consumption is far more extensive. Measuring in MWh allows for a more streamlined approach to understanding large-scale energy use, which is crucial for operational efficiency and cost management. For example, an industrial plant might consume around 1,000 MWh per month, necessitating the use of MWh for clarity and precision in reporting and planning.
Understanding when to use kWh versus MWh also aids in accurate billing. Misunderstanding these units can lead to significant discrepancies in energy bills and resource allocation. For instance, a power plant’s output is typically measured in MWh, which aligns with the scale of energy production and distribution.
In conclusion, recognizing the differences and appropriate applications of kWh and MWh is fundamental for effective energy management, whether you’re managing a household’s energy use or overseeing a large industrial operation. As we continue, we’ll explore practical tips for converting these units and avoiding common pitfalls in energy calculations.
Simple Tips for MWh to kWh Conversion
Converting megawatt-hours (MWh) back to kilowatt-hours (kWh) is a straightforward process, but it’s essential to understand the steps involved to ensure accuracy. This conversion is crucial for anyone dealing with energy consumption data, whether in residential or industrial contexts. Let’s break down the process into simple steps and highlight some common pitfalls to avoid.
Step-by-Step MWh to kWh Conversion
- Understand the Conversion Factor: The conversion between MWh and kWh is based on the metric system. Specifically, 1 MWh is equal to 1,000 kWh. This factor is grounded in the International System of Units, which standardizes measurements worldwide.
- Apply the Conversion Formula: To convert MWh to kWh, multiply the number of MWh by 1,000. For example, if you have 5 MWh, the conversion would be: 5 MWh × 1,000 = 5,000 kWh.
- Ensure Decimal Precision: When dealing with fractional MWh values, maintain decimal precision to avoid rounding errors. This is particularly important in large-scale energy projects where small discrepancies can lead to significant financial implications.
Common Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
While the conversion process is simple, there are common mistakes that can lead to errors:
- Confusing MWh with MW: Remember that MWh is a measure of energy, while MW (megawatt) is a measure of power. Mixing these up can lead to incorrect calculations and interpretations.
- Ignoring Units: Always double-check that the units are correctly labeled and calculated. Mislabeling can cause confusion, especially in documentation and reporting.
- Overlooking Precision: As highlighted earlier, maintaining precision is crucial. Use tools or calculators that support precise decimal handling to ensure accuracy.
By following these steps and being mindful of potential errors, you can effectively manage energy data and make informed decisions based on accurate conversions. As we continue, we’ll explore scenarios where these conversions play a vital role, particularly in large-scale energy analyses and renewable energy projects.
Working with Large Scale Conversions like Million kWh to MWh
Handling large-scale energy conversions, such as converting millions of kilowatt-hours (kWh) to megawatt-hours (MWh), is crucial in regional energy analyses and large-scale projects. These conversions are not merely academic; they are essential for efficient energy management, accurate reporting, and strategic planning in industries and regions.
Importance of Large Scale Energy Conversion
When dealing with regional energy consumption or production data, understanding how to convert large quantities of kWh to MWh is vital. For instance, a regional energy analysis might involve assessing the total electricity consumption of a city, which could easily reach millions of kWh. Converting this to MWh simplifies the data, making it more manageable and easier to communicate.
Consider a scenario where a city consumes 50 million kWh monthly. By converting this to MWh, you streamline the data to 50,000 MWh, providing a clearer perspective for policymakers and energy planners. This conversion is essential for budgeting, forecasting, and developing sustainable energy strategies.
Insights from Renewable Energy Nexus
Platforms like Renewable Energy Nexus offer valuable insights into large-scale renewable energy projects. Their resources help individuals and organizations understand the impact of renewable energy adoption at a macro level, offering guidance on integrating solar panels and other technologies to reduce reliance on conventional power sources.
Ensuring Calculation Accuracy
To keep calculations error-free, employ simplified ratio methods or specialized tools. Here’s a quick guide to ensure accuracy:
- Use the Correct Conversion Factor: Remember, 1 MWh equals 1,000 kWh. This ratio is the cornerstone of converting large-scale energy data.
- Implement Specialized Tools: Utilize energy management software or online calculators designed for large-scale conversions. These tools often include features that prevent common errors and ensure precise calculations.
- Double-Check Your Work: Always verify calculations manually or with a secondary tool to catch any discrepancies.
By understanding the significance of large-scale energy conversions and leveraging expert insights and tools, you can optimize energy management and planning. As we move forward, we’ll explore how technology simplifies these conversions, ensuring you have the tools needed for accurate energy accounting.
How to Use a kWh to MWh Calculator for Accurate Results
In today’s digital age, the task of converting kilowatt-hours (kWh) to megawatt-hours (MWh) has been significantly simplified through the use of online calculators and mobile apps. These tools offer a quick and efficient way to handle energy conversions, ensuring precision and saving time. But how do you ensure that these calculations are accurate and reliable?
Steps for Using a kWh to MWh Calculator
Before diving into the conversion process, it’s essential to gather some key information to ensure that the calculator provides accurate results. Here’s a checklist to guide you:
- Determine the Total kWh: Start by knowing the total kilowatt-hours you need to convert. This could be from your energy bill or an energy audit report.
- Access a Reliable Calculator: Choose a reputable online calculator or app designed specifically for energy conversions. Websites like A1 Solar Store offer user-friendly tools for this purpose.
- Input the Data: Enter the total kWh into the calculator. Most tools will automatically convert this to MWh by dividing the kWh value by 1,000.
- Review the Results: Once the conversion is complete, review the results to ensure they make sense in the context of your energy usage.
Benefits of Verifying with Manual Calculations
While calculators provide a quick solution, verifying results with manual math is crucial, especially for critical energy accounting. Here’s why:
- Ensure Accuracy: By manually applying the conversion formula (MWh = kWh / 1,000), you can confirm the calculator’s output.
- Identify Discrepancies: Manual verification helps catch any potential errors or discrepancies in the automated calculation, which is vital for financial and strategic planning.
- Develop Understanding: Performing the conversion manually enhances your understanding of the process, enabling better decision-making in energy management.
In conclusion, while kWh to MWh calculators are invaluable tools for simplifying energy conversions, combining their use with manual verification ensures the highest accuracy. As we progress, understanding these conversions will empower you to make informed decisions in both everyday and large-scale energy contexts.
Figuring Out Cost Implications with $ per kWh and $ per MWh
Understanding how costs are calculated at both kilowatt-hour (kWh) and megawatt-hour (MWh) levels is crucial for effective budgeting and forecasting. Whether you’re managing household expenses or overseeing industrial energy use, grasping these cost implications can lead to significant savings and more efficient energy consumption.
Calculating Costs at kWh and MWh Levels
To calculate the cost per kWh, you need to know your total energy bill and the total kWh consumed. For instance, if your monthly bill is $327 and your consumption is 2,500 kWh, your cost per kWh is calculated by dividing the bill amount by the kWh, resulting in approximately $0.12 per kWh. This straightforward calculation helps households track energy expenses and identify potential savings opportunities.
For larger-scale operations, such as industrial facilities, the cost per MWh becomes more relevant. Since 1 MWh equals 1,000 kWh, the cost per MWh can be derived by multiplying the cost per kWh by 1,000. This conversion is essential for industries to manage their energy budgets effectively and plan for future energy needs.
Tips for Converting $ per kWh to $ per MWh
- Understand Your Rates: Begin by ensuring you have accurate data on your current energy rates. This includes understanding peak-demand charges, which can significantly affect overall costs.
- Factor in Hidden Fees: Be aware of additional charges that might not be immediately apparent. These can include taxes, service fees, or seasonal rate adjustments.
- Use Energy Management Tools: Leverage tools and software that can help automate these calculations, providing real-time insights into your energy costs and helping you make informed decisions.
Identifying Hidden Costs and Charges
Hidden fees and charges can drastically alter your energy budget if not accounted for properly. Here are some common hidden costs to watch for:
- Taxes: Always check if taxes are included in your quoted rates or if they are added separately.
- Peak-Demand Charges: These charges apply during high-demand periods and can increase your bill significantly if not managed carefully.
- Service Fees: Some providers include additional service fees that can add up over time.
By understanding and managing these cost implications, you can optimize your energy expenditure, whether you’re a homeowner looking to reduce utility bills or an industrial manager aiming to streamline operational costs. As we continue, we’ll delve into more complex energy conversions and their implications for large-scale energy strategies.
Converting Electricity Rates from $ per MWh to $ per kWh
When managing energy costs, understanding how to convert electricity rates from $ per megawatt-hour (MWh) to $ per kilowatt-hour (kWh) is crucial. This conversion helps in making informed decisions about energy consumption and budgeting, especially when energy contracts or bills are quoted in different units. Let’s explore the step-by-step process for this conversion and highlight key factors to consider.
Step-by-Step Electricity Rate Conversion
Converting electricity rates from $ per MWh to $ per kWh involves a straightforward calculation:
- Understand the Conversion Factor: Since 1 MWh equals 1,000 kWh, the conversion factor is 1/1,000.
- Apply the Conversion Formula: To convert $ per MWh to $ per kWh, simply divide the cost per MWh by 1,000. For example, if your rate is $70 per MWh, the equivalent rate in $ per kWh would be $0.07.
- Verify the Calculation: Double-check your calculations to ensure accuracy, especially when these figures impact budget forecasts or contractual agreements.
Factors to Consider in Rate Conversion
Several factors can influence electricity rate conversions, and it’s important to be aware of these to maintain energy billing clarity:
- Contract Length: Long-term contracts might have fixed rates, while shorter contracts could be subject to market fluctuations.
- Market Fluctuations: Energy prices can vary based on demand, supply, and geopolitical factors. It’s crucial to consider these variations when planning your budget.
- Peak Demand Charges: Be aware of additional charges during peak usage times, which can significantly affect your overall cost.
Importance of Clarity in Energy Billing
Clarity in energy billing is essential for effective financial management and planning. Misunderstanding rate conversions can lead to budgeting errors and unexpected costs. By ensuring accurate conversions and understanding the components of your energy bill, you can optimize your energy expenditures and avoid potential pitfalls.
As we move forward, we’ll delve into more complex energy conversions and explore their implications for large-scale energy strategies, providing you with the knowledge to navigate the energy landscape effectively.

Exploring Advanced Factors Beyond kWh and MWh
As we delve deeper into the realm of energy conversions, it’s essential to explore more complex units like British thermal units (BTUs) per kilowatt-hour (kWh) and million BTUs (MMBTUs) per megawatt-hour (MWh). These advanced energy conversions are particularly relevant for industrial clients and those engaged in large-scale renewable energy adoption. But why are these conversions important, and how can they benefit your energy strategy?
Understanding Advanced Energy Conversions
In industrial settings, energy consumption is often measured in BTUs, a unit that represents the amount of energy required to heat one pound of water by one degree Fahrenheit. When dealing with large-scale energy projects, converting BTUs into kilowatt-hours or megawatt-hours can provide a clearer picture of energy efficiency and cost-effectiveness. For example, converting BTUs/kWh to MMBTUs/MWh helps industries quantify energy usage more accurately, facilitating better resource allocation and operational efficiency.
Here’s a simple conversion reference:
- 1 kWh = 3,412 BTUs
- 1 MWh = 3.412 MMBTUs
Relevance for Industrial Clients
For industrial clients, understanding these conversions is critical for optimizing energy use and reducing costs. Industries such as manufacturing, chemical processing, and large-scale data centers often operate on a scale where even small inefficiencies can lead to significant financial impacts. By utilizing advanced energy conversions, these industries can enhance their energy management strategies, leading to improved sustainability and reduced operational costs.
Adopting Renewable Energy Solutions
Incorporating renewable energy solutions is another area where advanced energy conversions play a crucial role. Platforms like Renewable Energy Nexus provide insights into integrating solar panels and other renewable technologies, reducing reliance on conventional grid power. By understanding how to convert energy units accurately, businesses can better assess the feasibility and benefits of renewable energy projects.
For instance, when planning a solar panel installation, knowing the conversion from BTUs to kWh can aid in determining the appropriate system size and potential energy savings. This level of precision ensures that renewable energy investments are both economically viable and environmentally sustainable.
In conclusion, mastering advanced energy conversions like BTUs to MMBTUs is essential for industrial clients and those pursuing large-scale renewable energy projects. By leveraging these insights, you can optimize energy use, enhance sustainability, and make informed decisions that align with your energy goals. As we continue, we’ll summarize the key takeaways from our exploration of kWh to MWh conversions and their broader implications.
Conclusion: Mastering Energy Conversion for a Sustainable Future
As we’ve journeyed through the intricacies of converting kilowatt-hours (kWh) to megawatt-hours (MWh), it’s clear that understanding these conversions is not just a technical exercise but a practical necessity. Whether you’re managing household energy bills or overseeing industrial energy strategies, mastering these conversions empowers you to make informed decisions that optimize energy use and reduce costs.
In everyday life, adopting clear energy conversion practices can lead to significant savings and efficiency improvements. For instance, knowing how to accurately convert your household’s energy consumption helps in tracking usage patterns and identifying areas for improvement. On a larger scale, industries can leverage these conversions to streamline operations, enhance sustainability, and ensure accurate billing.
Staying informed on renewable energy trends is equally crucial. As the global energy landscape shifts towards more sustainable practices, understanding the implications of these trends can position you at the forefront of innovation. Renewable energy sources like solar and wind are becoming increasingly viable, thanks to advancements in technology and supportive government policies. Platforms such as Renewable Energy Nexus offer invaluable insights and resources, helping you explore solar panel options to reduce dependency on traditional power grids.
By integrating renewable energy solutions, you not only contribute to a cleaner environment but also potentially lower your energy costs. Whether you’re considering solar panels for your home or evaluating large-scale renewable projects, the ability to navigate these energy conversions is a critical skill.
In conclusion, the mastery of kWh to MWh conversions and the embrace of renewable energy solutions are pivotal steps towards a sustainable future. As you continue to explore these areas, remember that informed decisions today can lead to a more efficient and environmentally friendly tomorrow. Keep abreast of emerging trends, utilize available resources, and take proactive steps in your energy journey. The future of energy is bright, and with the right tools and knowledge, you can play a part in shaping it.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Is 1000 kWh a MWh?
Yes, 1,000 kWh is equivalent to 1 MWh. This conversion is crucial for understanding energy consumption at different scales, such as moving from household usage to industrial levels.
2. How many kWh makes 1 MWh?
1 MWh is made up of 1,000 kWh. This conversion helps in scaling energy data from smaller units used in homes to larger units for industrial and regional energy management.
3. What is the difference between kW and MWh?
kW measures power, while MWh measures energy. 1 MWh equals 1,000 kWh, which is crucial for understanding energy usage over time, especially in large-scale operations.
4. How do I convert $ per MWh to $ per kWh?
To convert $ per MWh to $ per kWh, divide the MWh rate by 1,000. This conversion is essential for accurate energy budgeting and cost analysis.
5. Why is understanding kWh to MWh conversion important?
Converting kWh to MWh is vital for energy management, helping in accurate billing, resource planning, and optimizing energy efficiency in both residential and industrial settings.



