Introduction to Disadvantages of Wind Energy
Wind energy has emerged as a prominent player in the renewable energy landscape, harnessing the power of the wind through turbines to generate electricity. This method of energy production is celebrated for its sustainability and low environmental impact. However, while wind energy offers numerous advantages, it also comes with a set of disadvantages that are essential to consider. Understanding these drawbacks is crucial for stakeholders involved in both small-scale and large-scale energy projects.
One of the significant challenges associated with wind energy is its intermittency. Wind does not blow consistently; therefore, energy production can fluctuate. This unpredictability can complicate energy planning and grid management, necessitating backup systems or alternative energy sources to ensure a steady supply. As a result, wind energy is often not suitable as a standalone base load energy source.
Another critical factor is location constraints. Wind turbines require specific geographical conditions to operate efficiently, such as open plains or coastal areas with consistent wind patterns. Unfortunately, suitable sites are limited, and many ideal locations are often remote, which can pose logistical challenges for energy distribution and infrastructure development.
Lastly, the environmental impacts of wind energy cannot be overlooked. While wind energy does not produce greenhouse gas emissions during operation, the construction and installation of turbines can disrupt local ecosystems. Additionally, wind turbines have been linked to wildlife fatalities, particularly among birds and bats, raising concerns about biodiversity and habitat preservation.
In this article, we will delve deeper into the various disadvantages of wind energy, exploring their implications and how they affect the future of renewable energy projects. By acknowledging these challenges, we can work towards more informed and balanced energy strategies that incorporate wind energy responsibly.

Understanding What Are the Disadvantages of Wind Energy
While wind energy is often hailed as a clean and renewable source of power, it is not without its challenges. Understanding the disadvantages of using wind energy is crucial for anyone considering its implementation, whether on a small or large scale.
Intermittency
One of the most significant drawbacks is intermittency. Wind energy generation is highly dependent on wind conditions, which can vary greatly. This means that energy production is not constant; it can be high during windy periods and low or nonexistent during calm days. Such unpredictability complicates energy management, making it difficult to rely solely on wind energy as a primary power source. As a result, backup systems or alternative energy sources are often required to ensure a stable energy supply.
Location Constraints
Another challenge is the location constraints associated with wind turbines. These structures require specific geographical conditions to be effective. Ideal sites are typically open plains or coastal areas where wind patterns are consistent. However, suitable locations are limited, and many of them are remote, which can lead to increased costs for infrastructure development and energy distribution. The necessity for long transmission lines to connect these remote sites to urban areas can further complicate project feasibility.
Environmental Impacts
While wind energy is cleaner than fossil fuels, it does have environmental impacts that must be considered. The construction and installation of wind turbines can disrupt local ecosystems, causing habitat loss for various species. Additionally, wind turbines pose a risk to wildlife, particularly birds and bats, which can be killed by turbine blades. This raises ethical concerns regarding biodiversity and the preservation of natural habitats.
In summary, the disadvantages of wind turbine energy include intermittency, location constraints, and environmental impacts. These factors can significantly affect the feasibility and efficiency of wind energy projects. Understanding these challenges is essential as we explore the role of wind energy in our future energy strategies.
Examining Two Disadvantages of Wind Energy for Small-Scale Adoption
When considering the adoption of wind energy, homeowners and small businesses encounter specific challenges that can significantly influence their decisions. Two of the most notable obstacles are the upfront costs of wind energy and the availability of consistent wind resources.
Upfront Costs
Investing in wind energy systems involves substantial initial expenses. For residential wind turbines, costs can range from approximately $10,000 to $70,000, depending on factors such as turbine size, installation complexity, and site preparation needs. Even larger commercial turbines can run into the millions. These high upfront costs can deter potential users, especially in a market where financial incentives may not fully cover expenses. Although wind energy can lead to significant long-term savings—reducing electricity bills by 50-90%—the initial financial barrier remains a significant hurdle for many small-scale adopters (source).
Availability of Wind Resources
Another critical challenge is the availability of consistent wind resources. Wind energy generation is contingent upon having adequate wind speeds, which can vary greatly depending on geographical location. Areas with high wind potential, such as coastal regions or open plains, are not universally accessible. Homeowners and small businesses in less favorable locations may find it economically unviable to invest in a wind turbine system, as the energy output may not justify the costs. To determine whether a site is suitable for wind energy, potential users often need to conduct thorough assessments of local wind patterns and speeds, which can add to the complexity and cost of the project (source).
In conclusion, the upfront costs of wind energy and the challenges of small-scale wind energy adoption are significant considerations for homeowners and small businesses. Addressing these issues is essential for fostering broader acceptance and implementation of wind energy solutions. As we continue to explore the disadvantages of wind energy, it becomes clear that understanding these factors is crucial for making informed energy choices.
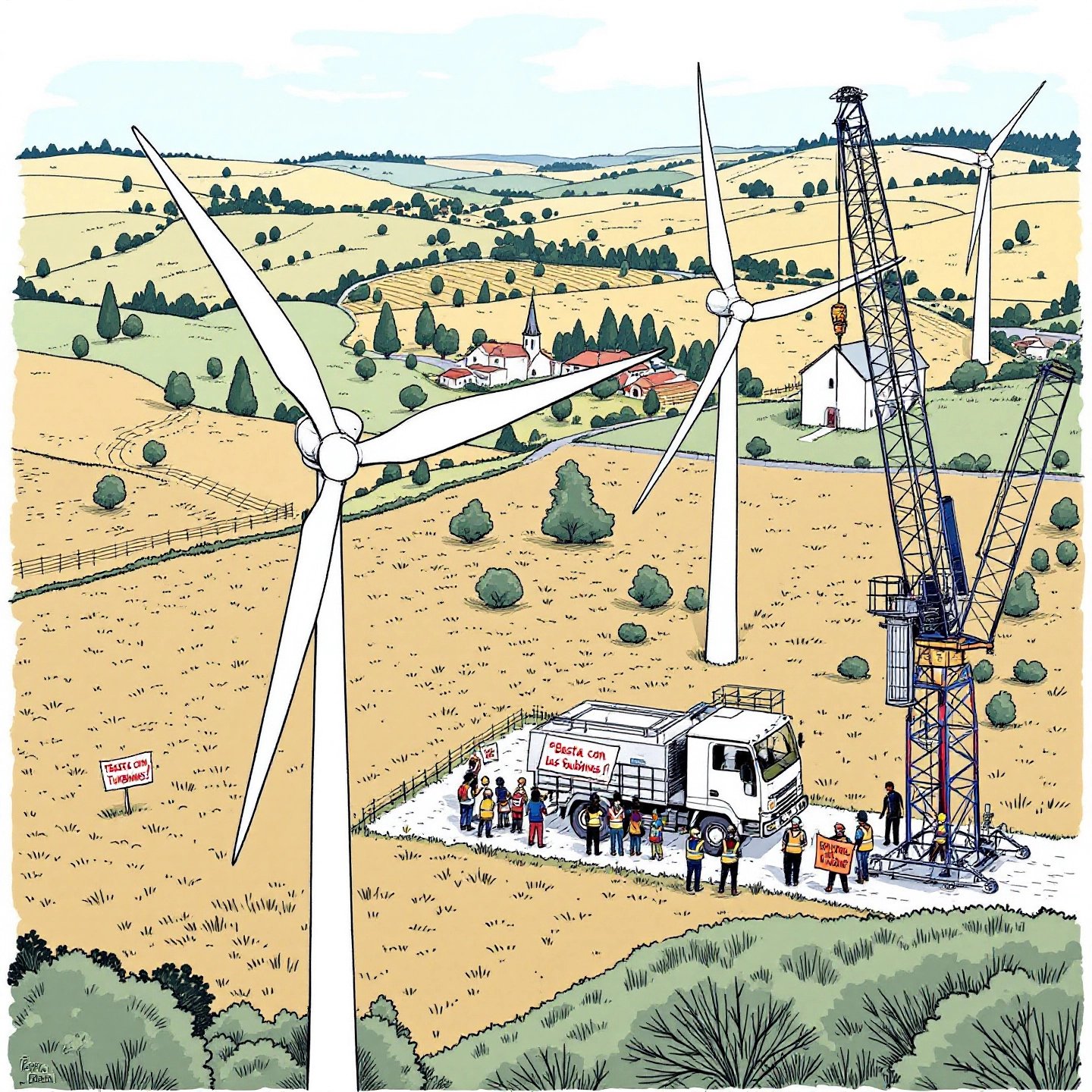
Highlighting Three Disadvantages of Wind Energy in Real-World Projects
While wind energy holds promise as a sustainable power source, its implementation in real-world projects often encounters significant challenges. These challenges can complicate development and hinder successful deployment, making it essential to understand the real-world wind energy challenges that affect both developers and communities.
Land Use Conflicts
One of the primary issues faced by wind energy projects is land use conflicts. Wind farms require substantial amounts of land, which can lead to disputes with local landowners, agricultural interests, and conservation groups. In many cases, suitable locations for wind turbines overlap with areas designated for agriculture or natural habitats, creating tension among stakeholders. For instance, farmers may be concerned about losing productive land, while environmentalists may oppose the disruption of wildlife habitats. These conflicts can delay project approvals and increase costs due to the need for negotiations and modifications to project plans.
Community Opposition
Another significant barrier is community opposition. Local residents may have concerns about the visual impact of turbines, noise pollution, and potential declines in property values. These concerns can lead to organized opposition groups that actively campaign against proposed wind projects, creating a challenging environment for developers. For example, in some regions, public sentiment has been so strong that it has resulted in moratoriums on new wind farm developments. Engaging with communities early in the planning process and addressing their concerns is crucial for overcoming this hurdle and fostering acceptance.
Maintenance Challenges
Moreover, the maintenance challenges associated with wind energy projects can complicate their long-term viability. Wind turbines require regular maintenance to ensure optimal performance and longevity. However, as turbines age, they may face increased technical problems, leading to higher operational costs. Additionally, the lack of skilled technicians can exacerbate these issues, particularly in remote locations where access to maintenance services is limited. For instance, offshore wind farms often struggle with maintenance due to the logistical difficulties of sending technicians out to sea. This can result in extended downtime for turbines, impacting energy production and profitability.
In summary, the disadvantages of wind energy in real-world projects include land use conflicts, community opposition, and maintenance challenges. These factors can complicate the development and deployment of wind farms, highlighting the need for comprehensive planning and community engagement to foster successful wind energy initiatives. As we move forward, understanding these challenges is vital for developing effective strategies that support the growth of wind energy while addressing the concerns of all stakeholders.
Addressing Five Disadvantages of Wind Energy for Long-Term Sustainability
Wind energy is often championed as a cornerstone of renewable energy initiatives, yet its limitations can significantly impact long-term sustainability goals. Understanding these disadvantages of wind energy is essential for developing a balanced energy strategy that meets both environmental and societal needs.
1. Environmental Disruption
While wind power is cleaner than fossil fuels, the construction and operation of wind turbines can lead to environmental disruption. The installation process can disturb local ecosystems, affecting soil composition and water drainage patterns. Additionally, the presence of wind farms can alter land use, potentially leading to habitat loss for various species. For instance, the construction of roads and facilities required for turbine access can fragment wildlife habitats, posing risks to local biodiversity.
2. Wildlife Impacts
The impact of wind energy on wildlife, particularly birds and bats, raises serious environmental concerns. Studies have shown that wind turbines can lead to fatalities among these species, primarily due to collisions with turbine blades. Although wind energy ranks lower in wildlife impact compared to other energy sources, ongoing research is necessary to mitigate these effects. Developers must prioritize careful site selection and technological advancements to reduce wildlife interactions.
3. Energy Storage Challenges
Another significant disadvantage is the challenge of energy storage. Wind energy generation is inherently intermittent, meaning that energy production does not always align with demand. As a result, effective energy storage solutions are crucial for balancing supply and demand. Currently, battery technology is still developing, and large-scale storage solutions remain expensive and limited in capacity. This can hinder the reliability of wind energy as a primary power source.
4. Grid Reliability
Integrating wind energy into existing power grids presents grid reliability challenges. Wind farms often produce energy in remote locations far from population centers, necessitating extensive transmission infrastructure to deliver electricity where it is needed. This can lead to increased costs and complications in grid management, particularly during periods of low wind. Upgrading the grid to accommodate renewable energy sources is essential but can be a complex and costly process.
5. Resource Allocation
Lastly, the allocation of resources for wind energy projects can divert attention and funding from other renewable energy initiatives. This resource allocation issue may hinder the development of diverse energy portfolios that include solar, geothermal, and other renewable sources. A balanced approach is vital to ensure that investments in wind energy do not come at the expense of other sustainable technologies.
In conclusion, while wind energy offers significant benefits, its disadvantages must be carefully considered to ensure long-term sustainability. Addressing environmental disruption, wildlife impacts, energy storage challenges, grid reliability, and resource allocation will be pivotal in shaping a responsible energy future. As we continue to explore the long-term sustainability of wind energy, it is crucial to develop strategies that mitigate these challenges, paving the way for a more resilient energy landscape.

Exploring Environmental Disadvantages of Wind Power Generation
Wind energy is often lauded for its potential to provide clean, renewable power. However, it is essential to recognize that the environmental disadvantages of wind energy can pose significant challenges to ecosystems and wildlife. Understanding these impacts is crucial for responsible wind energy development.
Habitat Interference
One of the primary environmental concerns related to wind energy is habitat interference. The construction and operation of wind turbines can disrupt local ecosystems. This disruption can lead to habitat loss for various species, particularly in areas where wind farms are built on previously undisturbed land. For instance, the development of access roads and turbine pads can fragment habitats, making it difficult for wildlife to thrive. Additionally, the presence of turbines can alter natural landscapes, potentially displacing sensitive species and affecting their migration patterns.
Noise Pollution
Another significant issue is noise pollution. Wind turbines generate sound during operation, which can affect both wildlife and nearby human populations. The noise produced by turbine blades moving through the air can disturb local fauna, particularly species that rely on sound for communication and navigation. For example, birds may avoid areas with high noise levels, leading to reduced breeding success and altered migration routes. In residential areas, the noise from turbines can also lead to complaints from residents, raising concerns about the overall acceptance of wind energy projects.
Impact on Wildlife
The impact of wind energy on wildlife is a pressing concern, particularly regarding birds and bats. Studies have shown that collisions with turbine blades can result in fatalities for these species, raising ethical questions about biodiversity conservation. While wind energy is generally considered to have a lower impact on wildlife compared to fossil fuel sources, ongoing research is necessary to mitigate these effects. Developers must prioritize careful site selection and implement measures such as radar systems to detect and deter wildlife from approaching turbines (source).
In summary, the environmental disadvantages of wind energy, including habitat interference, noise pollution, and wildlife impacts, highlight the need for careful planning and consideration in wind energy development. By addressing these issues proactively, it is possible to create wind energy projects that are both sustainable and respectful of local ecosystems. As we delve deeper into the challenges of wind energy, understanding these environmental impacts will be crucial for developing effective strategies that promote responsible energy practices.
Evaluating the Economic Disadvantages of Wind Energy Investment
As the world shifts towards renewable energy, wind energy stands out as a promising solution. However, it is crucial to recognize the economic disadvantages of wind energy that can impede its widespread adoption. Understanding these financial challenges is particularly important for stakeholders in developing regions where resources may be limited.
High Initial Capital Costs
One of the most significant barriers to wind energy investment is the high initial capital costs. The expenses associated with purchasing wind turbines, site preparation, and installation can be substantial. For instance, a medium-scale turbine with a capacity of around 2 MW can cost between $2.18 million and $4.13 million, depending on various factors such as location and installation requirements (source). These costs can deter potential investors, especially in regions where financial incentives for renewable energy are lacking.
Variable Maintenance and Operational Costs
Beyond the initial investment, the variability of maintenance and operational costs adds another layer of complexity. While wind energy has low operational costs compared to fossil fuels, these expenses can fluctuate based on factors like turbine age, location, and the need for skilled labor. Regular maintenance is essential for ensuring optimal performance, but it can be more challenging and costly in remote areas where access to technicians is limited. This variability can create uncertainty for investors and developers, complicating financial planning.
Long-Term Financial Viability
Moreover, the long-term financial viability of wind energy projects can be affected by the intermittency of wind resources. Unlike traditional power plants that can generate electricity on demand, wind energy production is dependent on weather conditions. This unpredictability necessitates the development of energy storage solutions or backup systems, which can further increase project costs. In developing regions, the lack of infrastructure for energy storage can exacerbate these financial challenges, limiting the feasibility of wind energy projects.
In conclusion, while wind energy presents a sustainable alternative to fossil fuels, its economic disadvantages—including high initial capital costs, variable maintenance expenses, and concerns over long-term viability—must be carefully considered. Addressing these financial challenges is essential for fostering broader adoption of wind energy, particularly in developing regions where the potential for growth is significant. As we continue to explore the complexities of wind energy, understanding the economic landscape will be vital for shaping effective strategies in renewable energy investment.
Comparing the Disadvantages of Wind Energy with Solar and Geothermal Sources
As the world increasingly turns to renewable energy sources, it is essential to understand the disadvantages of wind energy in comparison to other alternatives like solar and geothermal energy. Each energy source has its unique set of challenges that can affect its viability and implementation. Below, we will explore the main drawbacks of wind energy alongside those of solar and geothermal energy in a comparative format.
| Energy Source | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Wind Energy |
|
| Solar Energy |
|
| Geothermal Energy |
|
In summary, while wind energy is a promising renewable resource, it faces challenges such as intermittency, location constraints, and wildlife impact. Similarly, solar energy grapples with its dependence on sunlight and high installation costs, while geothermal energy is hindered by its high upfront investment and geological limitations. Understanding these disadvantages of solar energy and disadvantages of geothermal energy alongside wind energy is crucial for stakeholders to make informed decisions about energy sourcing and development.
As we continue to explore the complexities of renewable energy, it is evident that a balanced approach that considers the unique challenges of each source is essential for a sustainable energy future. In the next section, we will summarize the overall disadvantages of wind energy and reflect on its implications for future energy strategies.
Summarizing the Overall Disadvantages of Wind Energy for Future Outlook
As we explore the landscape of renewable energy, wind energy stands out for its potential to provide clean, sustainable power. However, it is crucial to acknowledge the disadvantages of wind energy, which can significantly influence its effectiveness and adoption in future energy strategies.
Firstly, the intermittency of wind energy is a major concern. Unlike fossil fuels, which can provide a constant energy supply, wind energy generation is highly dependent on wind conditions. This unpredictability can complicate energy planning and necessitate backup systems, making it less reliable as a primary power source.
Secondly, location constraints pose significant challenges. Ideal wind farm sites are often remote, requiring extensive infrastructure to connect them to urban centers where energy is needed. This not only increases costs but can also lead to land use conflicts with local communities and environmental groups.
Environmental impacts, particularly concerning wildlife, are another critical disadvantage. Wind turbines can pose threats to birds and bats, resulting in fatalities that raise ethical concerns about biodiversity and habitat preservation. While wind energy is cleaner than fossil fuels, the ecological footprint of turbine installation and operation cannot be overlooked.
In addition to these factors, the economic challenges associated with wind energy, such as high initial capital costs and variable maintenance expenses, further complicate its viability. These financial barriers can deter investment, particularly in developing regions where resources are scarce.
In conclusion, while wind energy offers a promising alternative to traditional energy sources, its disadvantages must be carefully considered in the context of future energy strategies. Addressing issues of intermittency, location constraints, environmental impacts, and economic challenges is essential for fostering a balanced and sustainable approach to energy development. As research and innovation continue to evolve, understanding these drawbacks will be crucial for shaping a more resilient energy landscape.
Conclusion to Disadvantages of Wind Energy
As we explore the landscape of renewable energy, wind energy stands out for its potential to provide clean, sustainable power. However, it is crucial to acknowledge the disadvantages of wind energy, which can significantly influence its effectiveness and adoption in future energy strategies.
Firstly, the intermittency of wind energy is a major concern. Unlike fossil fuels, which can provide a constant energy supply, wind energy generation is highly dependent on wind conditions. This unpredictability can complicate energy planning and necessitate backup systems, making it less reliable as a primary power source.
Secondly, location constraints pose significant challenges. Ideal wind farm sites are often remote, requiring extensive infrastructure to connect them to urban centers where energy is needed. This not only increases costs but can also lead to land use conflicts with local communities and environmental groups.
Environmental impacts, particularly concerning wildlife, are another critical disadvantage. Wind turbines can pose threats to birds and bats, resulting in fatalities that raise ethical concerns about biodiversity and habitat preservation. While wind energy is cleaner than fossil fuels, the ecological footprint of turbine installation and operation cannot be overlooked.
In addition to these factors, the economic challenges associated with wind energy, such as high initial capital costs and variable maintenance expenses, further complicate its viability. These financial barriers can deter investment, particularly in developing regions where resources are scarce.
In conclusion, while wind energy offers a promising alternative to traditional energy sources, its disadvantages must be carefully considered in the context of future energy strategies. Addressing issues of intermittency, location constraints, environmental impacts, and economic challenges is essential for fostering a balanced and sustainable approach to energy development. As research and innovation continue to evolve, understanding these drawbacks will be crucial for shaping a more resilient energy landscape.
Frequently Asked Questions about Wind Energy Disadvantages
1. What are examples of disadvantages of wind energy?
Disadvantages of wind energy include intermittency, location constraints, and environmental impacts such as wildlife fatalities and habitat disruption.
2. What is the biggest con to wind energy?
The most significant con of wind energy is its intermittency; wind does not blow consistently, leading to fluctuating energy production.
3. How do location constraints affect wind energy projects?
Wind turbines require specific geographical conditions, often found in remote areas, which complicates infrastructure development and energy distribution.
4. What environmental impacts are associated with wind energy?
Wind energy can disrupt local ecosystems, lead to habitat loss, and pose risks to wildlife, particularly birds and bats, due to collisions with turbine blades.
5. Are the economic disadvantages of wind energy significant?
Yes, high initial capital costs and variable maintenance expenses can deter investment in wind energy, especially in developing regions.



