Introduction to Biomass Pros and Cons
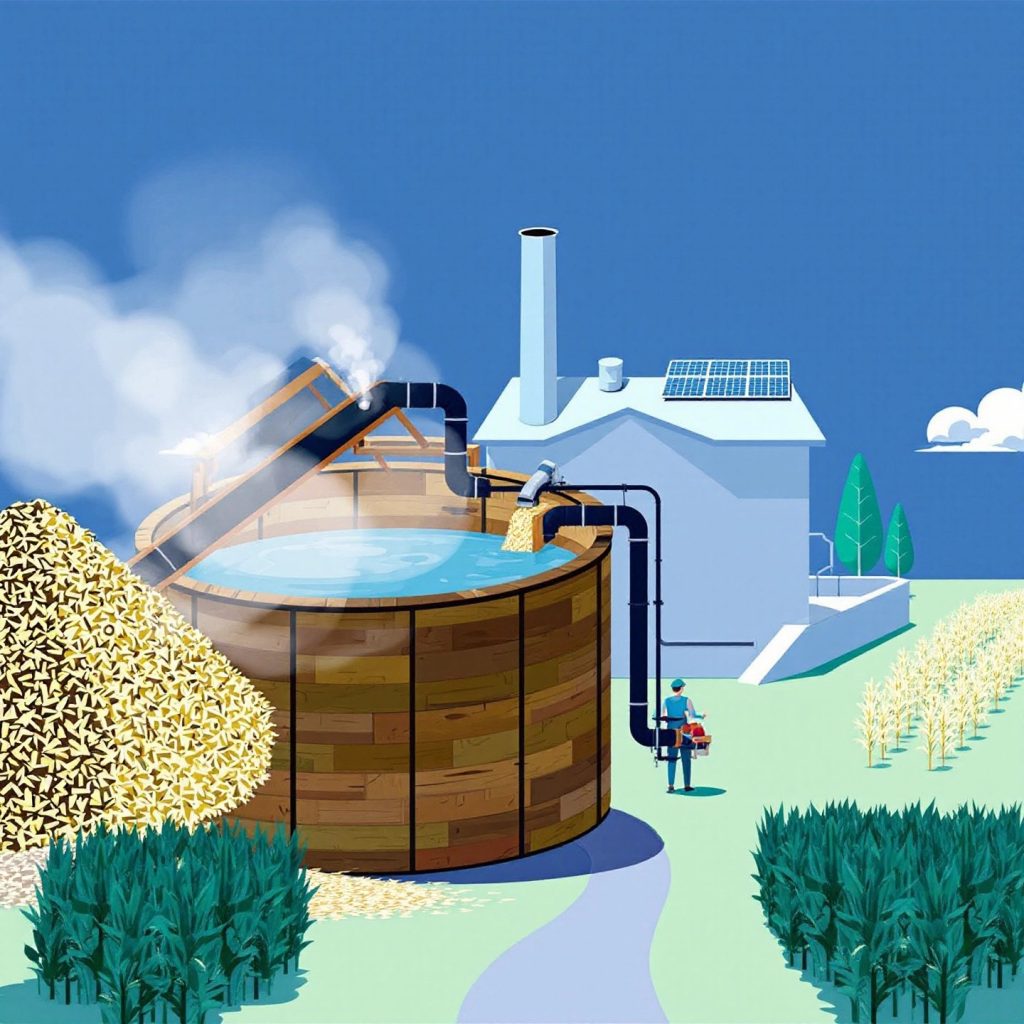
Imagine a world where your leftovers and garden waste power your home. Sounds intriguing, right? This is the promise of biomass energy—a renewable energy source that has been utilized since the earliest humans discovered fire. Biomass energy, derived from organic materials like plants and waste, plays a significant role in today’s renewable energy landscape. To fully appreciate its potential, it is crucial to understand both the advantages and disadvantages that come with it.
This article aims to provide a comprehensive biomass energy overview, detailing the benefits and challenges of using biomass as a clean energy source. By examining the pros and cons, you will gain insights into how biomass fits into the broader context of renewable energy solutions. As we delve into the complexities of biomass, we will explore how it can contribute to sustainable energy goals and what considerations must be taken into account to harness its full potential effectively.
Throughout this exploration, you’ll notice that while biomass offers exciting possibilities, it also presents unique challenges. Understanding these nuances is key to making informed decisions about its use and integration into our energy systems. So, let’s dive into the world of biomass and discover how it can be both a boon and a challenge in our quest for clean energy.
Understanding the Basics of Biomass
Have you ever wondered how organic waste can be transformed into energy? This is the essence of biomass energy, a concept that has been around since humans first harnessed fire. But what exactly is biomass? Simply put, biomass is organic material that comes from plants and animals. It includes a variety of feedstocks such as wood pellets, agricultural residues like corn stalks, and even animal manure. These materials are rich in energy, initially captured from the sun through photosynthesis, which can be converted into usable power.
Biomass energy basics involve using these organic materials to produce heat, electricity, or biofuels. For example, wood and wood processing wastes are commonly used as biomass feedstocks. They are burned directly to produce heat or converted into biofuels like ethanol through chemical processes such as fermentation. Similarly, agricultural residues and other biogenic materials in municipal solid waste can be processed to generate energy, reducing reliance on fossil fuels and minimizing waste in landfills.
So, what are the pros and cons of biomass energy? On the positive side, biomass is a renewable resource that can help reduce waste and decrease greenhouse gas emissions when managed sustainably. However, it also presents challenges such as the need for significant land use and potential emissions during combustion. Understanding these biomass energy basics is crucial for evaluating its role in our energy future. As we move forward, exploring how biomass fits into the broader landscape of renewable energy will be essential for making informed decisions about its use.

Major Advantages of Biomass Energy
Imagine turning everyday waste into a valuable energy source that powers your community. This is one of the many biomass energy pros that make it an appealing option in the renewable energy sector. One of the most significant advantages of biomass is its ability to reduce waste. By converting organic materials like agricultural residues, wood waste, and even animal manure into energy, biomass helps decrease the amount of waste sent to landfills. This not only minimizes environmental impact but also reduces the costs associated with waste disposal and landfill management.
Another compelling benefit is the potential for carbon neutrality. Biomass energy is often considered carbon neutral because the carbon dioxide released during combustion is roughly equal to the amount absorbed by the plants during their growth. This cycle can significantly reduce greenhouse gas emissions compared to fossil fuels, contributing to climate change mitigation efforts.
Biomass also plays a crucial role in supporting rural economies. The production and processing of biomass create job opportunities in areas that often face economic challenges. From harvesting and transporting feedstocks to operating biomass facilities, the industry supports a range of employment opportunities. According to the USDA, removing woody biomass from forests not only aids in forest health but also boosts local economies by creating jobs.
Moreover, biomass can be produced locally, which can lower transportation costs and reduce reliance on imported fuels. This local production capability ensures that energy needs can be met using resources readily available in the community, enhancing energy security and resilience.
While these advantages make biomass an attractive energy option, it’s essential to balance them with potential challenges. In the next section, we’ll delve into the key disadvantages and challenges associated with biomass energy to provide a comprehensive view of its role in clean energy solutions.
Key Disadvantages and Challenges
While biomass energy offers numerous benefits, it also presents significant challenges that must be addressed to maximize its potential. One of the primary biomass energy cons is the concern over land use. Large-scale biomass production often requires substantial land, which can lead to deforestation and loss of biodiversity if not managed sustainably. This competition for land can also impact food production, leading to higher prices and potential food shortages.
Another challenge is the fluctuation in feedstock supply. Biomass resources are often seasonal, and their availability can vary due to weather conditions and agricultural cycles. This inconsistency can lead to supply chain disruptions and increased costs for biomass facilities. Additionally, the transportation of biomass feedstock, which is often bulky and heavy, can be costly and energy-intensive, further complicating logistics and increasing operational expenses.
Emissions during combustion are another critical issue. While biomass is considered more environmentally friendly than fossil fuels, burning biomass still releases carbon dioxide and other pollutants. To mitigate these emissions, it is essential to adopt advanced combustion technologies and ensure that biomass is sourced sustainably. This includes using feedstocks that do not compete with food production and are harvested in ways that do not harm the environment.
Furthermore, the upfront costs associated with biomass energy projects can be prohibitive. The initial investment in infrastructure, such as biomass boilers and conversion facilities, is often high, and financing can be challenging due to the perceived risks and fluctuating market conditions. According to the 2024 Guide to Sustainable Biomass Sourcing, developing a robust strategy for sustainable sourcing is crucial to overcoming these economic hurdles and ensuring the long-term viability of biomass projects.
Addressing these challenges requires a comprehensive approach that includes policy support, technological innovation, and community engagement. By understanding and tackling these challenges of biomass, we can better integrate biomass into the renewable energy landscape and contribute to a more sustainable future. In the next section, we will explore how biomass is converted into electricity, highlighting the technologies that make this process possible.
How Biomass Powers Electricity Grids
Imagine harnessing the energy from organic materials to power entire communities. This is the promise of biomass electricity, an innovative approach to renewable energy that utilizes various technologies to convert biomass into power. At the core of biomass power generation are methods like direct combustion, gasification, and co-firing with coal, each offering unique advantages and challenges.
Direct Combustion
Direct combustion is the most common method for generating biomass electricity. It involves burning biomass materials, such as wood chips or agricultural residues, to produce steam. This steam drives a turbine connected to a generator, producing electricity. The simplicity of this process makes it widely used, but it does require careful management of emissions to minimize environmental impact.
Gasification
Gasification offers a more advanced approach by converting biomass into a synthesis gas through partial oxidation. This gas can then be used in a gas turbine or engine to generate electricity. The benefit of gasification is its higher efficiency compared to direct combustion, as well as its ability to produce fewer emissions. However, it requires more complex technology and infrastructure.
Co-firing with Coal
Co-firing involves burning biomass alongside coal in existing power plants. This method allows for a gradual transition to renewable energy by utilizing existing infrastructure, reducing costs, and lowering emissions compared to coal-only operations. However, the availability and cost of biomass feedstock can be a limiting factor.
While biomass power offers the advantage of dispatchability—being controllable and available on demand—it also faces challenges such as feedstock procurement and emissions management. By understanding these technologies and their implications, we can better appreciate the role of biomass electricity in the renewable energy landscape. As we continue, we’ll explore how biomass heating solutions compare to conventional systems, providing further insight into its practical applications.

Adopting Biomass for Heating Solutions
Imagine a heating system that not only warms your home but also contributes to sustainability. This is the promise of biomass heating, which uses organic materials to generate heat. But how do biomass boilers stack up against conventional heating systems like gas or oil boilers? Let’s explore the pros and cons of using biomass boilers for both residential and commercial applications.
Pros of Biomass Boilers
- Renewable and Carbon Neutral: Biomass boilers use wood pellets, chips, or logs, which are renewable resources. When sourced sustainably, the carbon dioxide released during combustion is balanced by the carbon absorbed during the plants’ growth, making it a carbon-neutral process.
- Cost-Effective: Biomass fuel is generally cheaper than fossil fuels, and its price is more stable, protecting you from the volatility of oil and gas markets. For those with access to local wood supplies, the cost savings can be significant.
- Energy Independence: Biomass boilers offer an off-grid heating solution, reducing reliance on centralized utilities. This is particularly beneficial in rural or remote areas where access to gas networks may be limited.
- Incentives and Long-Term Savings: In regions like the UK, financial incentives such as the Renewable Heat Incentive can offset initial costs, making biomass boilers a financially attractive option over time.
Cons of Biomass Boilers
- High Initial Costs: The upfront investment for biomass boilers can be substantial, often higher than traditional systems. This includes the cost of the boiler itself and the necessary infrastructure for fuel storage and handling.
- Space Requirements: Biomass systems require significant space for both the boiler and the fuel. This can be a limiting factor for homes or businesses with limited space.
- Maintenance and Supply Challenges: Regular maintenance is needed to keep biomass boilers running efficiently, including cleaning and ash disposal. Additionally, ensuring a consistent supply of quality biomass fuel can be challenging, especially in urban areas.
While biomass boilers present a promising alternative to conventional heating systems, they are not without challenges. Understanding these pros and cons is essential when considering biomass heating for your home or business. As we continue, we’ll delve into the environmental implications and sustainability of biomass energy, further exploring its role in our quest for a greener future.
Environmental Implications and Sustainability
Imagine a future where our energy needs are met without compromising the planet’s health. Biomass energy, with its potential for carbon neutrality, is often seen as a beacon of hope in the renewable energy sector. But how sustainable is it really? Let’s delve into the environmental impact of biomass and explore its role in achieving sustainability goals like net-zero emissions.
Carbon Footprint and Net-Zero Goals
Biomass is frequently touted as a carbon-neutral energy source. This is because the carbon dioxide (CO2) released during biomass combustion is roughly balanced by the CO2 absorbed by plants during their growth. According to the U.S. Energy Information Administration, this cycle can help reduce the overall carbon footprint compared to fossil fuels. However, the true sustainability of biomass depends on how it is sourced and managed.
In the quest for net-zero emissions, responsibly sourced biomass can play a significant role. By using waste materials from agriculture and forestry, we can avoid the environmental degradation associated with purpose-grown biomass crops, which often require extensive land use and can lead to deforestation and biodiversity loss. The World Resources Institute highlights the importance of sustainable sourcing to ensure that biomass contributes positively to climate goals.
Sustainable Sourcing and Management
For biomass to be truly sustainable, it must be sourced from materials that do not compete with food production or lead to land degradation. This includes using agricultural residues, forestry by-products, and municipal waste. Sustainable management practices, such as planting fast-growing trees and using efficient harvesting methods, are essential to maintain soil health and ecological balance.
The potential for biomass to support decarbonization is significant. The Lawrence Livermore National Lab estimates that sustainable biomass supply could remove up to 884 million tons of CO2 annually by 2050, equivalent to emissions from about 200 million cars. However, this potential can only be realized with strict adherence to sustainability principles and standards.
As we consider the environmental implications of biomass, it is crucial to balance its benefits with the challenges of responsible management. For those exploring comprehensive renewable solutions, platforms like Renewable Energy Nexus provide valuable insights and resources to help navigate the complexities of clean energy transitions. By prioritizing sustainability, we can harness the power of biomass to support a greener, more sustainable future.
Comparing Biomass to Other Renewable Options
When it comes to choosing a renewable energy source, understanding the differences between options like biomass, solar, and wind is crucial. Each has its own set of advantages and challenges, and the best choice often depends on specific needs and local conditions. Let’s dive into a comparison of biomass versus solar and wind energy, focusing on cost, accessibility, and environmental impact.
Cost Considerations
Cost is a significant factor when selecting an energy source. Biomass generally requires a lower initial investment compared to solar, which involves high upfront costs for panels and installation. However, solar energy can offer lower long-term costs due to minimal maintenance and the potential for energy savings over time. Wind energy, while also costly to install, benefits from decreasing prices and is often competitive with other renewables in terms of cost per kilowatt-hour.
Accessibility and Availability
Accessibility varies significantly among these energy sources. Biomass is often more accessible in rural areas where organic waste is abundant, providing a reliable energy source that isn’t weather-dependent. Solar energy, on the other hand, requires consistent sunlight, making it less effective in regions with frequent cloud cover or short daylight hours. Wind energy’s effectiveness hinges on location, as it requires areas with consistent wind patterns to be viable.
Environmental Impact
Environmental impact is a critical consideration in the renewable energy debate. Biomass can be carbon-neutral if sourced sustainably, but it does produce emissions during combustion and can lead to deforestation if not managed properly. Solar energy boasts a low environmental footprint during operation but raises concerns about the disposal of hazardous materials used in panels. Wind energy is one of the cleanest options, with minimal emissions, but it can affect local wildlife and ecosystems.
| Factor | Biomass | Solar | Wind |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cost | Lower initial cost | High upfront cost, low long-term cost | Decreasing installation costs |
| Accessibility | Rural areas with organic waste | Sunny regions | Windy locations |
| Environmental Impact | Potential emissions, deforestation risk | Low operational impact, disposal concerns | Minimal emissions, wildlife impact |
In summary, the choice between biomass, solar, and wind energy involves weighing various factors, including cost, accessibility, and environmental impact. Each option has its strengths and weaknesses, and the ideal choice often depends on the specific circumstances and goals of the user. As we move forward in exploring renewable energy solutions, understanding these differences can help guide informed decisions.
Practical Steps for Making Biomass Work Effectively
Imagine transforming your organic waste into a reliable energy source right at your doorstep. Sounds complex? It’s simpler than you might think. Implementing biomass energy effectively requires understanding best practices for feedstock sourcing and system maintenance. Let’s explore how you can harness this renewable energy source efficiently and sustainably.
Best Practices for Feedstock Sourcing
- Local Sourcing: Prioritize sourcing biomass locally to reduce transportation costs and emissions. This not only supports local economies but also ensures a steady supply of feedstock.
- Diversification: Use a mix of feedstocks such as agricultural residues, wood chips, and organic waste to ensure consistent supply and reduce dependency on a single source.
- Sustainability: Ensure that feedstocks are sustainably harvested. This involves using residues and by-products that do not compete with food production or contribute to deforestation.
System Maintenance and Optimization
- Regular Maintenance: Implement a routine maintenance schedule for biomass systems to ensure they operate efficiently. This includes cleaning boilers and checking emissions controls to prevent system failures.
- Technology Upgrades: Stay updated with the latest technology improvements, such as advanced combustion systems and emissions controls, to enhance system performance and reduce environmental impact.
- Data Monitoring: Use data-driven analysis to monitor system performance and identify areas for improvement. This can help optimize operations and reduce costs over time.
For those interested in a comprehensive approach to renewable energy, platforms like Renewable Energy Nexus offer valuable resources and insights. By integrating biomass with other renewable solutions, you can achieve a multi-pronged strategy that enhances energy efficiency and sustainability.
Incorporating these best practices into your biomass energy strategy not only maximizes its benefits but also ensures a sustainable and efficient energy solution. As we conclude our exploration of biomass, reflect on how these practices can be adapted to your specific needs and circumstances, paving the way for a cleaner, greener future.
Conclusion
As we wrap up our exploration of biomass energy, it’s clear that this renewable resource holds significant promise, yet also presents considerable challenges. Biomass energy offers a unique opportunity to turn waste into power, contribute to carbon neutrality, and support rural economies. However, its implementation is not without hurdles, such as land-use concerns, emissions, and high initial costs.
In this biomass energy conclusion , it is crucial to weigh these pros and cons carefully. The potential for biomass to reduce waste and provide a reliable energy source is compelling, but it requires sustainable practices and careful management to avoid negative environmental impacts. The key to unlocking the full potential of biomass lies in responsible sourcing, technological innovation, and community engagement.
Before deciding to adopt biomass energy, consider your specific context and needs. Evaluate the availability of local feedstocks, the infrastructure required, and the environmental regulations in place. This balanced approach ensures that biomass can be a viable component of a diversified renewable energy strategy.
Ultimately, understanding the biomass pros and cons summary empowers you to make informed decisions. As we strive for a sustainable future, integrating biomass with other renewable solutions can pave the way for cleaner energy landscapes. Embrace the potential of biomass, but do so with an eye toward sustainability and innovation.
Frequently Asked Questions about Biomass Energy
1. What are the pros and cons of biomass energy?
Biomass energy is renewable and can reduce waste and emissions. However, it poses challenges like land use, feedstock supply issues, and initial costs.
2. How does biomass energy impact the environment?
Biomass can be carbon-neutral if sourced sustainably, but it may lead to emissions and deforestation if not managed properly.
3. Is biomass energy cost-effective compared to other renewables?
Biomass has lower initial costs than solar but may incur higher operational costs due to feedstock and maintenance needs.
4. What are the main uses of biomass energy?
Biomass is used for electricity generation, heating, and as biofuels, offering versatility in applications, especially in rural areas.
5. How can biomass contribute to sustainability goals?
Biomass supports sustainability by reducing reliance on fossil fuels and utilizing waste, provided it adheres to sustainable sourcing practices.



