Introduction to Batteries in Parallel vs Series
When setting up battery systems, understanding the difference between battery connections in parallel and series battery setup is crucial for optimizing performance and longevity. These configurations determine how the voltage and capacity of a battery system will behave, affecting everything from small gadgets to large renewable energy systems.
In a series battery setup, batteries are linked in a chain, with the positive terminal of one battery connected to the negative terminal of the next. This configuration increases the total voltage of the system while keeping the capacity unchanged. For instance, connecting two 6V batteries in series results in a 12V system, which is ideal for applications requiring higher voltage, such as powering electric vehicles or certain industrial equipment.
Conversely, battery connections in parallel involve linking all positive terminals together and all negative terminals together. This maintains the system’s voltage at the level of a single battery but increases the overall capacity. For example, connecting three 12V 100Ah batteries in parallel results in a 12V 300Ah system. This setup is beneficial for applications that demand longer battery life, like off-grid renewable energy systems or RV power supplies.
Understanding these configurations is vital for selecting the right setup for your needs. Whether you’re powering a solar energy system, an off-grid cabin, or everyday electronic devices, choosing the appropriate battery configuration can enhance efficiency and performance. By grasping the basics of voltage and capacity, you can make informed decisions that optimize your energy setup and ensure reliable power delivery.
Understanding Core Differences Between Series And Parallel
When it comes to configuring batteries, the choice between series and parallel connections can significantly impact your energy system’s performance. So, what exactly happens in each setup?
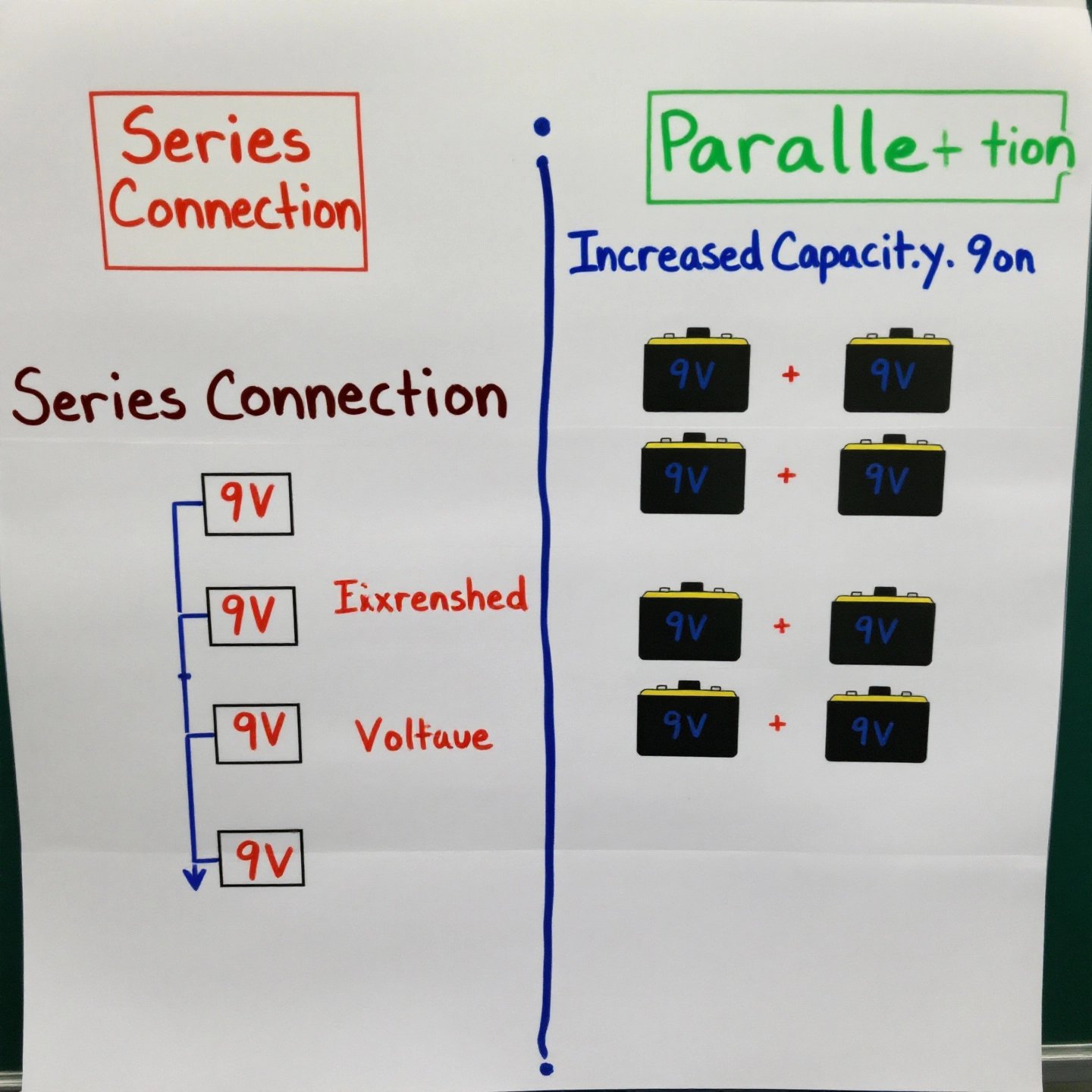
Series Connection: Boosting Voltage
Imagine you’re setting up a system where higher voltage is crucial. In a series connection, batteries are linked end-to-end. This means the positive terminal of one battery is connected to the negative terminal of the next. The result? A cumulative increase in voltage while the capacity remains unchanged. For instance, connecting two 12V batteries in series will yield a total voltage of 24V, but the amp-hour capacity stays the same as a single battery. This configuration is particularly useful in applications like electric vehicles and certain industrial machines where higher voltage is a necessity. However, it’s important to note that if one battery fails in a series, it can affect the entire chain, potentially leading to a system failure.
Parallel Connection: Enhancing Capacity
On the flip side, when you need more capacity rather than voltage, a parallel connection is the way to go. Here, all positive terminals are connected together, and all negative terminals are linked. This setup maintains the voltage of a single battery but increases the overall capacity. For example, connecting three 12V 100Ah batteries in parallel results in a system with 12V but a capacity of 300Ah. This is advantageous for applications that require prolonged power delivery, such as RVs, solar storage, and backup systems. Moreover, if one battery fails in a parallel setup, the rest of the system can continue to function, providing a layer of redundancy.
Both configurations have their unique strengths and are tailored for different applications. Whether you’re powering a solar array, an RV, or a backup energy system, understanding these core differences will help you choose the right setup for optimal performance. As you delve deeper into battery configurations, you’ll find that selecting the right setup not only enhances efficiency but also ensures the longevity of your energy system.
Examining Voltage And Capacity In Various Configurations
When configuring battery systems, understanding the interplay between voltage and capacity is crucial for device performance. Imagine needing to power a system where both voltage and capacity must be optimized. How do different configurations like 12v batteries in series or 6v battery in parallel impact the performance?
12V Batteries in Series: Doubling the Voltage
Consider a scenario where you have two 12V batteries. By connecting them in series, you effectively double the voltage to 24V, while the capacity remains at the level of a single battery. This setup is particularly beneficial for applications requiring higher voltage, such as electric vehicles or certain industrial equipment. The increased voltage allows for more efficient power delivery over long distances with minimal voltage drop, which can be critical in maintaining device performance. However, a key consideration is that if one battery fails in this series setup, the entire system is compromised, potentially leading to a complete shutdown.
6V Batteries in Parallel: Enhancing Capacity
On the other hand, if your priority is extending the duration of power supply, connecting 6v batteries in parallel can be advantageous. In this configuration, the voltage remains at 6V, but the capacity is multiplied by the number of batteries. For instance, two 6V 100Ah batteries in parallel will maintain a 6V output but double the capacity to 200Ah. This is ideal for applications like RVs and solar energy systems, where prolonged power availability is essential. Moreover, the redundancy offered by a parallel setup ensures that if one battery fails, the others continue to supply power, providing reliability in critical situations.
Choosing between these configurations depends heavily on your specific energy needs. Whether you’re aiming to maximize voltage or capacity, understanding these principles allows you to tailor your battery setup to suit particular applications efficiently. This knowledge not only optimizes performance but also extends the lifespan of your battery system, ensuring you make the most out of your energy investment.
As you consider your options, remember that the right configuration can significantly impact both efficiency and cost-effectiveness. Whether you’re setting up a renewable energy system or powering everyday devices, these insights into voltage and capacity configurations are invaluable.
Setting Up Batteries Safely For Optimal Performance
When it comes to configuring your battery setup, safety is paramount. Whether you’re connecting batteries in series or parallel, understanding the correct battery safety setup and wiring techniques is essential to ensure optimal performance and prevent potential hazards.
Essential Safety Gear and Precautions
Before diving into the setup, equip yourself with the right safety gear. Always wear approved safety glasses or goggles, and consider a face shield for additional protection. Proper clothing can shield your skin from accidental spills or sparks. Ensure your workspace is well-ventilated to avoid the build-up of explosive gases, especially when dealing with lead-acid batteries. Auto Battery Safety and Handling guidelines emphasize the importance of avoiding ignition sources like cigarettes and open flames near batteries.
Step-by-Step Wiring Techniques
- Series Connection: Start by connecting the positive terminal of one battery to the negative terminal of the next. Continue this pattern until all batteries are linked. This setup increases the voltage of your system while maintaining the same capacity.
- Parallel Connection: Connect all positive terminals together and all negative terminals together. This increases the capacity of your system while keeping the voltage the same.
When arranging batteries, use high-quality cables and connectors to ensure stable and efficient connections. Avoid loose or frayed wires, as these can cause short circuits. For more insights on proper electrical wiring, check out these best practices.
Voltage Checks and Hazard Prevention
Regular voltage checks are crucial to maintaining battery health. Use a multimeter to verify that the voltage levels are as expected. Overcharging can lead to overheating and battery damage, so use a charge controller to regulate the charging process. Be aware of potential hazards like short circuits, which can occur if metal tools accidentally bridge battery terminals. Always handle tools carefully and store them away from battery terminals.
By following these steps and precautions, you can ensure a safe and efficient battery setup. Remember, a well-planned configuration not only optimizes performance but also extends the lifespan of your batteries, safeguarding your investment. As we move forward, understanding the practical implications of these setups in real-world scenarios can further enhance your energy solutions.
Common Wiring Methods And Connection Tips
When setting up battery systems, understanding the nuances of wiring batteries in series vs. parallel can significantly influence both performance and longevity. Let’s explore typical scenarios and essential considerations for each configuration.
Wiring Batteries in Series
Imagine you need to increase the voltage of your system. Wiring batteries in series is your go-to method. This involves connecting the positive terminal of one battery to the negative terminal of the next. By doing so, you effectively add up the voltages of each battery while maintaining the same capacity. For instance, connecting four 12V batteries in series will yield a total system voltage of 48V, ideal for applications like electric vehicles or high-voltage solar systems. However, it’s crucial to ensure all batteries have the same voltage and capacity to avoid imbalances that could lead to system failure.
Wiring Batteries in Parallel
On the flip side, if extending the capacity is your priority, parallel wiring is your best choice. In this setup, all positive terminals are connected together, and all negative terminals are linked. This maintains the voltage of a single battery but multiplies the capacity. For example, connecting three 12V 100Ah batteries in parallel results in a 12V 300Ah system, perfect for long-duration power supply needs like off-grid cabins or RVs. The redundancy in parallel setups ensures that if one battery fails, the others continue to supply power, providing reliability.
Essential Connection Tips
- Wire Gauge Selection: Choose the correct wire gauge to handle the current load without overheating. Thicker wires are required for higher current applications. Using the right gauge prevents voltage drops and ensures efficient power delivery.
- Terminal Connectors: Use high-quality connectors to ensure secure and stable connections. Loose or corroded connectors can lead to increased resistance and potential power loss.
- Layout Tips: Arrange batteries in a manner that minimizes cable lengths and reduces resistance. This not only improves efficiency but also helps in maintaining balanced connections, which is critical for the health and longevity of your battery bank.
To maintain balanced connections, especially in parallel setups, ensure that all batteries are equally charged before connecting them. This prevents imbalances that could lead to uneven wear and premature battery failure. Regular maintenance checks, like cleaning terminals and checking voltage levels, are essential to keep your system running smoothly.
By following these wiring and connection tips, you can optimize your battery setup for both efficiency and longevity. As we delve into real-world applications in the next section, you’ll see how these principles are applied across various systems to achieve reliable and efficient power solutions.
Real World Applications Of 12v And 6v Systems
In the realm of energy storage, choosing between 12v systems applications and 6v systems uses can significantly impact your setup’s efficiency and functionality. Let’s explore how these configurations are utilized across various real-world scenarios.
12V Systems: Versatility and Power
12V systems are renowned for their versatility, making them a staple in numerous applications. For instance, in the world of recreational vehicles (RVs), 12V batteries are often employed to power essential appliances like refrigerators, lights, and air conditioning units. The higher voltage allows for efficient energy distribution across the vehicle, ensuring that all systems function optimally during long trips. Additionally, 12V setups are favored in larger solar power systems, where they provide a robust solution for storing substantial amounts of energy, crucial for off-grid living or backup power solutions.
Another common application is in automotive industries, where 12V batteries are the standard for starting engines and powering electrical systems. Their widespread availability and compatibility make them an easy choice for vehicle manufacturers and consumers alike.
6V Systems: Compact and Cost-Effective
On the other hand, 6V batteries are often chosen for applications where compact size and cost-effectiveness are paramount. Golf carts frequently use 6V batteries connected in series to achieve the desired voltage while maintaining a manageable size and weight. This configuration allows for smooth operation over extended periods, which is essential for a leisurely day on the golf course.
In smaller solar setups, 6V batteries can be an economical choice for homeowners looking to dip their toes into renewable energy without a hefty initial investment. These systems are particularly suitable for cabins or small-scale projects where energy demands are lower, yet reliability is still a priority.
Choosing the Right System
When deciding between 12V and 6V systems, consider factors such as the scale of your project, energy requirements, and budget constraints. For those looking to power larger systems or requiring more versatile energy solutions, 12V configurations are often the best fit. In contrast, 6V systems offer a more compact and budget-friendly option for smaller applications.
By understanding the specific needs of your application, you can select the battery configuration that offers the best balance of performance, cost, and convenience. As we continue to explore battery setups, remember that the right choice not only enhances efficiency but also ensures the longevity and reliability of your energy system.

How To Charge Batteries In Parallel Or In Series
Charging batteries effectively is crucial for maintaining their health and ensuring optimal performance, whether you’re dealing with charging batteries in series or charging batteries in parallel. Let’s explore the best practices for each setup.
Charging Batteries in Series
When charging batteries in series, the primary goal is to ensure that each battery receives the same amount of current. This is because the voltage of the entire system is the sum of the individual battery voltages. Therefore, a charger that matches the total voltage of the series setup is essential. For instance, if you have two 12V batteries in series, you’ll need a 24V charger to efficiently charge the system.
It’s important to use a charger with a balancing feature to prevent any single battery from being overcharged or undercharged, which can lead to reduced battery life or failure. Additionally, always monitor the charging process to ensure that the voltage does not exceed the manufacturer’s recommended limits, as this can cause overheating and potential damage.
Charging Batteries in Parallel
In a parallel setup, all batteries share the same voltage, so a charger that matches the voltage of a single battery is sufficient. The advantage here is that if one battery reaches full charge, the others can continue charging without risk of overcharging the first. This setup also allows for flexibility, as you can add more batteries to increase capacity without changing the charger.
When charging batteries in parallel, it’s crucial to use a charger that can handle the total capacity of the system. For example, if you have three 12V 100Ah batteries in parallel, a charger capable of handling 300Ah is ideal. Ensuring that the charger has a proper cutoff feature will prevent overcharging and extend the lifespan of your batteries.
Voltage Considerations and Timeframes
Regardless of the setup, always consider the voltage and current ratings of your batteries and charger. Overcharging is a common issue that can lead to overheating and reduced battery life. Therefore, using a smart charger with automatic cutoff features is recommended to maintain the health of your battery system.
Timeframes for charging can vary based on the capacity and current output of the charger. A slower charge rate is generally better for battery health, as it minimizes heat generation and stress on the battery cells. For lithium-ion batteries, charging to about 80% capacity instead of 100% can also help prolong their lifespan.
By understanding these charging principles and selecting the right equipment, you can ensure that your battery system operates efficiently and safely. As you advance to the next section, consider how these charging strategies fit into your overall energy management plan.
Avoiding Typical Mistakes And Ensuring Safety
When configuring battery systems, even minor errors can lead to significant issues. Imagine the frustration of a system failure due to something as simple as incorrect polarity or mismatched battery capacities. Let’s explore some common battery connection mistakes and how to practice safe battery handling to ensure your setup remains efficient and hazard-free.
Common Mistakes in Battery Connections
- Wrong Polarity: Connecting the positive terminal to the negative can cause severe damage. For example, in automotive applications, this mistake might result in a blown fuse or a damaged alternator, as seen in real-life scenarios where such errors led to costly repairs (source).
- Mismatched Capacities: Using batteries of different capacities in the same setup can lead to uneven charging and discharging, causing some batteries to wear out faster than others. This imbalance not only affects performance but also poses safety risks.
- Improper Wiring Sequences: Incorrect wiring can lead to short circuits, which are dangerous and can result in battery damage or even fire hazards. Always follow the correct sequence and double-check your connections.
Safe Battery Handling Practices
- Use Protective Gear: Always wear safety goggles and gloves when handling batteries to protect against acid spills and sparks.
- Regular Inspections: Routinely check battery terminals for corrosion and ensure all connections are tight. Loose connections can lead to increased resistance and overheating.
- Proper Tools and Equipment: Use insulated tools to prevent accidental short circuits. Ensure that your workspace is free from metal objects that could accidentally bridge battery terminals.
- Documentation and Diagrams: Keep a detailed diagram of your battery setup. This helps in troubleshooting and ensures that any maintenance or modifications are done correctly.
By avoiding these common mistakes and adhering to safe handling practices, you can significantly reduce the risk of damage and enhance the reliability of your battery system. As we move to the final chapter, we’ll recap the key insights and emphasize the importance of understanding battery configurations for optimal energy management.
Maintaining Long Term Reliability With Proper Care And Checks
Ensuring the longevity and reliability of your battery system hinges on a comprehensive battery maintenance routine. Regular checks and proper care can significantly extend a battery’s life, enhancing performance and preventing unexpected failures.
Essential Maintenance Practices
- Voltage Level Checks: Regularly check the voltage levels of your batteries using a multimeter. A fully charged lead-acid battery should read around 12.6 to 12.8 volts. Any significant deviation could indicate a potential issue, such as a failing cell or a charging system problem.
- Cleaning Terminals: Corroded terminals can lead to poor connections and reduced efficiency. Use a mixture of baking soda and water to clean terminals, followed by a thorough rinse and drying. Applying a thin layer of petroleum jelly can help prevent future corrosion.
- Battery Balancing: Especially important in parallel setups, ensuring all batteries are equally charged prevents imbalances that can lead to premature failure. Consider using a battery balancer or equalizer to maintain uniform charge levels across your battery bank.
Advanced Checks: Capacity and Load Testing
- Capacity Checks: Conduct regular capacity tests to determine the actual capacity of your batteries compared to their rated capacity. This helps in identifying aging batteries that may no longer hold a full charge, allowing for timely replacements.
- Load Testing: Perform load tests to ensure your battery can handle the expected power demands. This involves applying a load to the battery and measuring its ability to maintain voltage under stress. A battery that cannot sustain voltage during a load test may need replacement.
Prolonging Battery Lifespan
Proper maintenance not only enhances performance but also extends the battery lifespan care. Following these routines can prevent common issues such as sulfation in lead-acid batteries, which occurs when batteries are left discharged for extended periods. For lithium-ion batteries, avoiding full discharges and keeping them at a moderate state of charge when not in use can significantly prolong their life (Battery University).
By integrating these maintenance practices into your routine, you can ensure your battery system remains reliable and efficient. As we conclude, remember that a well-maintained battery setup not only saves costs but also provides peace of mind, knowing your energy needs are securely met.
Conclusion
As we wrap up our exploration of batteries in parallel vs series, it’s clear that understanding these configurations is essential for optimizing your energy setup. Each chapter has delved into the nuances of battery connections, highlighting how they impact voltage, capacity, and overall system performance. Whether you’re dealing with a small-scale application or a large renewable energy project, the insights gained here can guide you in making informed decisions.
Firstly, recognizing the fundamental differences between series and parallel connections is key. A series connection increases voltage, making it suitable for applications requiring higher power, while a parallel connection boosts capacity, ideal for extended usage scenarios. This knowledge allows you to tailor your setup to specific needs, enhancing battery efficiency and ensuring reliable power delivery.
Moreover, practical applications in real-world scenarios, such as RVs, solar systems, and automotive uses, demonstrate how these configurations can be applied for maximum benefit. The choice between 12V and 6V systems, for example, hinges on factors like energy requirements and budget, influencing both efficiency and cost savings with batteries.
Safety and maintenance are also paramount. Proper setup techniques, regular checks, and adherence to safety protocols can prevent common pitfalls and extend battery lifespan. By avoiding typical mistakes and ensuring balanced connections, you safeguard your investment and enhance system reliability.
Ultimately, the insights provided here equip you to optimize your energy solutions effectively. Whether you’re a DIY enthusiast or a professional, applying these principles can lead to significant improvements in energy management. For those seeking further guidance, consulting with experts or utilizing resources like Renewable Energy Nexus can provide additional support in selecting the right products and configurations for your needs.
FAQs about Batteries in Parallel vs Series
1. Is it better to put batteries in parallel or series?
The choice depends on your needs. Series increases voltage, suitable for high-power applications like electric vehicles. Parallel increases capacity, ideal for longer power supply in RVs or solar storage. Consider efficiency and application requirements when deciding.
2. Can you wire two batteries in series and parallel at the same time?
Technically, you can’t connect each battery in both series and parallel simultaneously. However, you can have sets of batteries connected in series, with those sets then connected in parallel to combine benefits of both configurations.
3. What happens if you connect batteries with different capacities?
Connecting batteries of different capacities can cause imbalances, leading to uneven charging and discharging. This can reduce battery life and efficiency, potentially causing one battery to overwork and fail prematurely.
4. How do you safely charge batteries in series?
Use a charger that matches the total voltage of the series setup. Ensure the charger has a balancing feature to prevent overcharging. Monitor charging to avoid exceeding voltage limits, which can cause damage.
5. What is the advantage of using a 12V system over a 6V system?
A 12V system offers greater versatility and efficiency for high-demand applications like RVs and solar power setups. It provides robust power delivery, while 6V systems are more compact and cost-effective for smaller projects.